library construction
1.1 DNA Library Construction
The construction of DNA library components is the foundation of second-generation sequencing technology. The essence of DNA library construction is to convert large genomic DNA fragments of the sample to small fragments of DNA, and then add sequencing adapters to the small fragments of DNA molecule Liangu Dan to form an effective library molecule that can be sequenced on the machine.The process of constructing a DNA library mainly includes five steps: DNA fragmentation, end repair, A-tail addition, splice connection, and PCR enrichment.
The construction of a second-generation sequencing RNA library is mainly divided into mRNA library, lncRNA library, small RNA library, etc. according to the type of RNA.The construction process of mRNA and lncRNA libraries includes:RNA enrichment, RNA fragmentation, cDNA first strand synthesis, second strand synthesis, PCR enrichment.RNA enrichment is a necessary step in the construction of mRNA and lncRNA libraries, as rRNA accounts for over 80% of the total RNA. Without rRNA extraction, the sequencing data of mRNA and lncRNA libraries mostly contain rRNA related data, which is not conducive to a comprehensive and in-depth analysis of mRNA and lncRNA expression differences and sequence changes.The construction process of Small RNA libraries differs slightly from that of mRNA and lncRNA libraries, mainly including 3 'connector connection and blocking, 5' connector connection, cDNA synthesis, and PCR enrichment.
2.cfRNA
In the face of cancer, "treating diseases before they occur" is particularly important, and effective early diagnosis is of great help to cancer treatment:The five-year survival rate of patients diagnosed early is 5-10 times higher than that of late stage patients.Therefore, early detection of cancer can provide patients with the best chance of cure.At present, even though early diagnostic techniques are not yet mature worldwide, a highly specific and sensitive detection method that is easy to popularize is the bottleneck for early cancer diagnosis and screening. Liquid biopsy technology is a highly anticipated early detection technique for cancer, with biomarkers including circulating tumor cells (CTC), extracellular DNA (cfDNA) and its methylation, extracellular RNA (cfRNA), exosomal proteins, etc.Compared with CTC/cfDNA, cfRNA as a cancer biomarker has at least three advantages: 1. Sensitivity and functionality: RNA can actively enter the extracellular environment through cell efflux mechanisms, such as exosomes. Therefore, biomarkers based on cfRNA not only have many signals appearing in the patient's plasma in the early stages of cancer, but also can provide more functional information. 2. Organizational specificity: The expression of many RNAs (including human and microbial sources) is tissue-specific, therefore, changes in the expression profile of specific RNAs in different tumors can be reflected in the plasma.3. Low cost: Effective cfRNA sequencing targeting cancer signals has lower costs compared to cfDNA and its methylation sequencing, which is more beneficial for the popularization of early screening and diagnosis.On July 11, 2022, the Lu Zhi team from the School of Life Sciences collaborated with medical and research personnel from multiple institutions, including Wang Pengyuan's team from Peking University First Hospital and Xu Zhenjiang's team from Nanchang University, to publish a research paper titled "Cancer type classification using plasma cell-free RNAs derived from human and microbes" in the authoritative biomedical journal eLife, Reported the application and prospects of extracellular RNA (cfRNA) in early diagnosis of pan cancer.
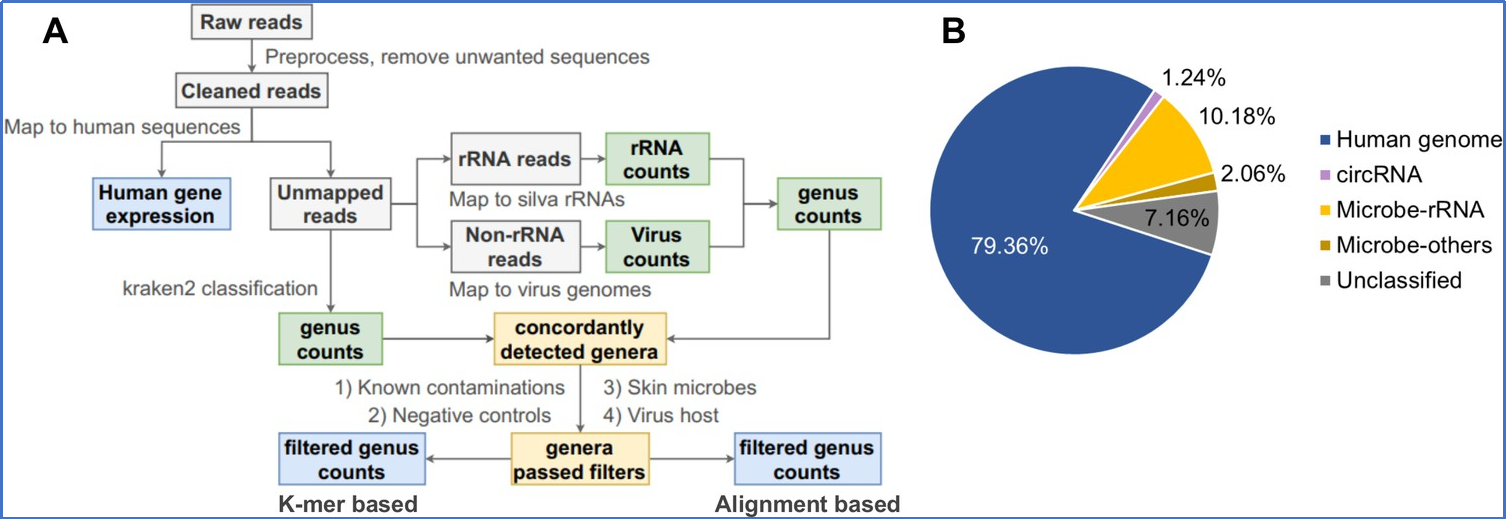
Fig.1 Research Methods and Route
Research has found that using longer and more trace cfRNAs (including mRNA, lncRNA, circRNA, etc.) in addition to small RNA in human plasma, and integrating bioinformatics analysis and machine learning models, can effectively diagnose the five common cancers (colon cancer, gastric cancer, liver cancer, esophageal cancer, lung cancer), with an AUC (area under the curve) of 0.91 (especially liver cancer, which can reach 0.95 or above).It is worth mentioning that this study particularly emphasizes research on early cancer (over 65% of cases belong to early tumors), and even in all early case cohorts, the diagnostic AUC can still reach 0.9, revealing the value of cfRNA in early cancer diagnosis.In addition, on the basis of human derived cfRNA, if combined with microbial derived cfRNA, cancer tissue types can be more accurately distinguished.
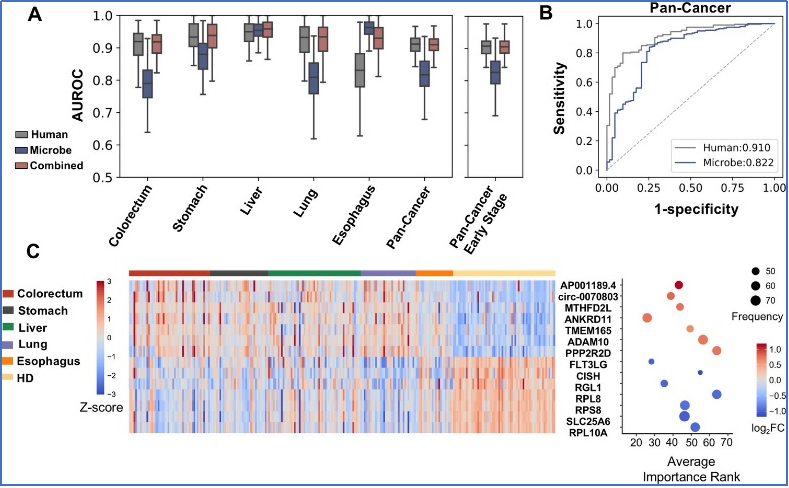
Fig.2 cfRNA can be used for cancer diagnosis


